
Cureus What S The Risk Differentiating Risk Ratios Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios
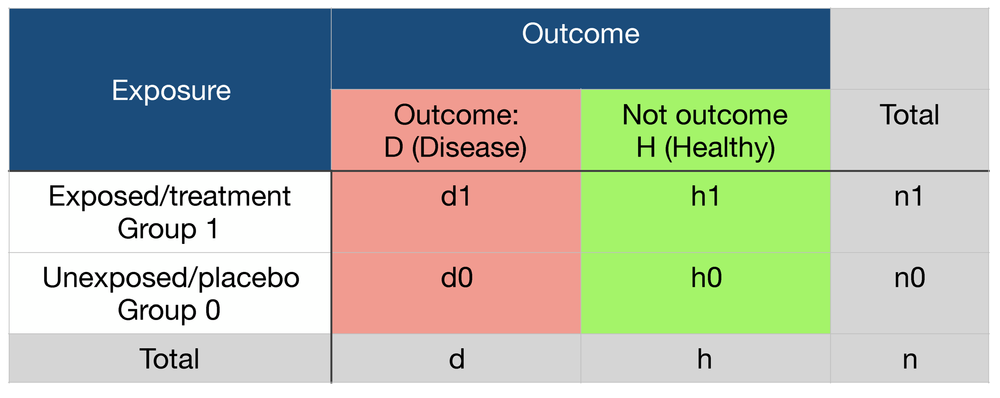
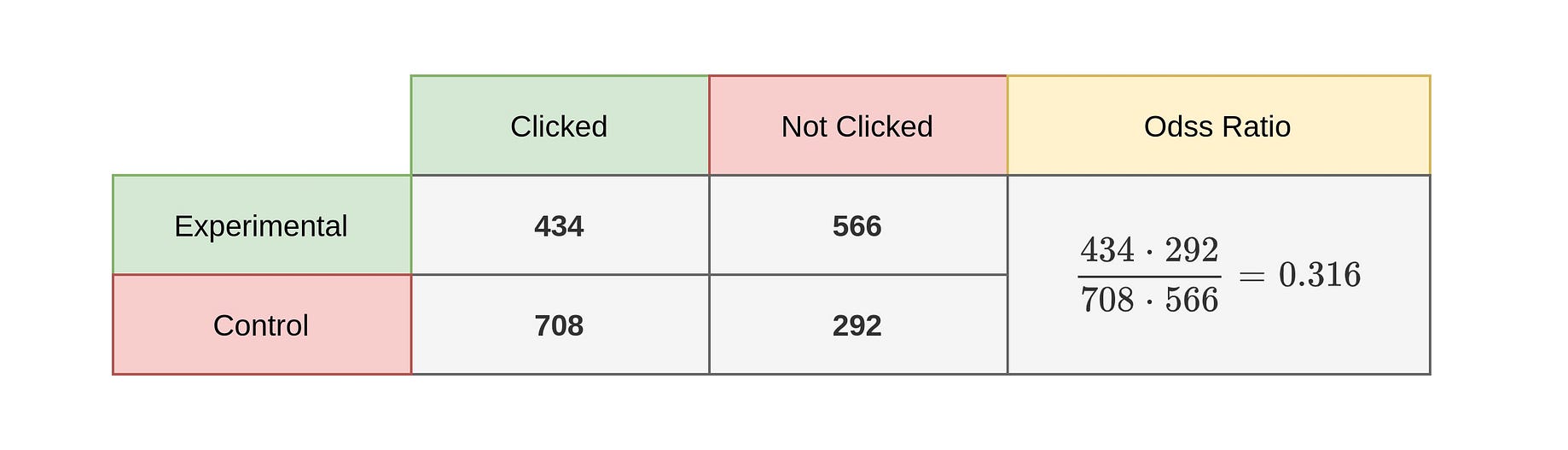
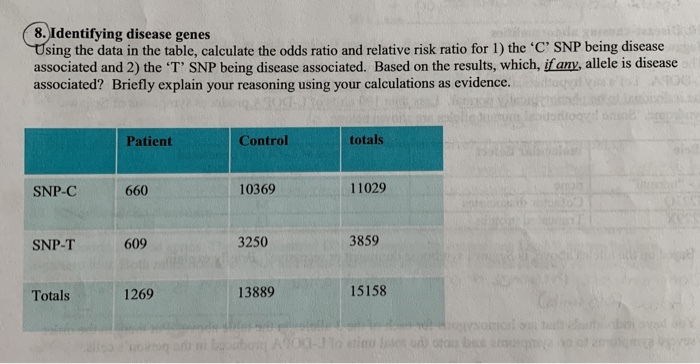
For estimates of odds ratios, this is logit (ie the logarithm of the odds of the mean); We often use the odds ratio and relative risk when performing an analysis on a 2by2 table, which takes on the following format The odds ratio tells us the ratio of the odds of an event occurring in a treatment group to the odds of an event occurring in a control groupIt is calculated as Odds ratio = (A*D) / (B*C) The relative risk tells us the ratio of the probability of
Odds ratio vs relative risk
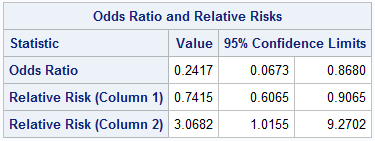
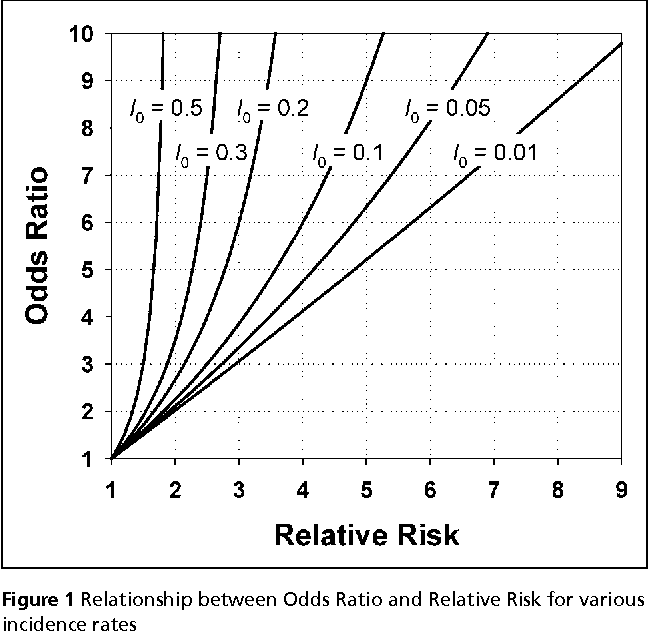
Odds ratio vs relative risk-Relative risk Probability is the likelihood of an event in relation to all possible events If a horse wins 2 out of every 5 races, its probability of winning isWhen the disease is rare, the odds ratio will be a very good approximation of the relative risk The more common the disease, the larger is the gap between odds ratio and relative risk In our example above, p wine and p no_wine were 0009 and 0012 respectively, so the odds ratio was a good approximation of the relative risk OR = 0752 and RR = 075

Relative Risks And Odds Ratios What S The Difference Mdedge Family Medicine
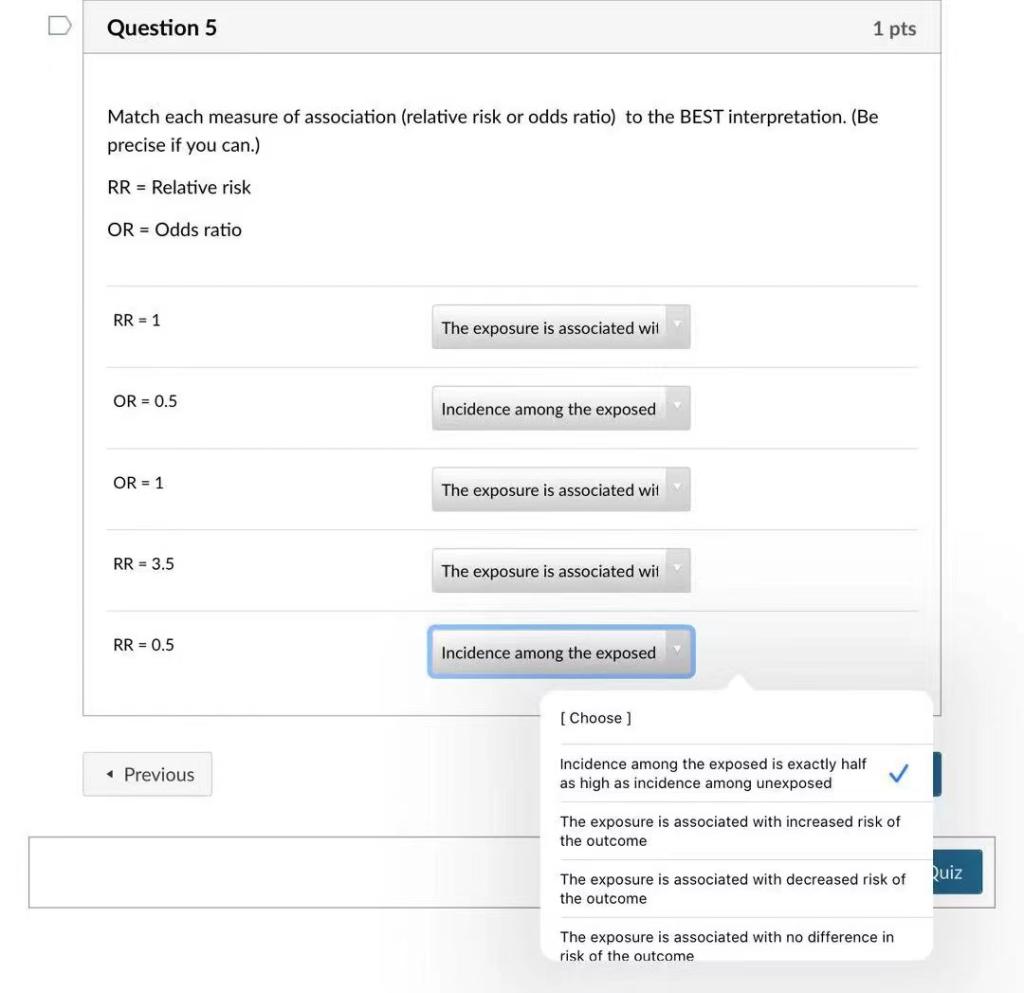
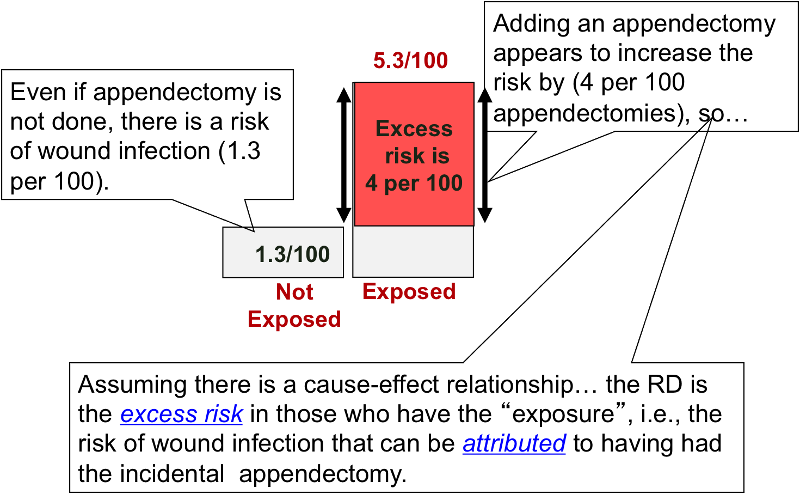
Both the odds ratio and the relative risk compare the relative likelihood of an event occurring between two groups The relative risk is easier to interpret and is consistent with general intuition Some designs, however, allow only for the calculation of the odds ration Covariate adjustment is easier for an odds ratio The odds ratio will be greater than the relative risk if the relative risk is greater than one and less than the relative risk otherwise In the example above, if the adjusted odds ratio were interpreted as a relative risk, it would suggest that the risk of antibiotic associated diarrhoea is reduced by 75% for the intervention relative to theCould someone explain why odds ratios are used in case control studies where as relative risk is used in RCT and cohort studies?
For estimates of relative risk ratios, this becomes logarithm We can specify this manually, or just use a builtin family for our generalized linear model for which the logarithm is the canonical link fucntion, and hence the default Odds ratio vs risk ratio You know the difference between risk and odds A risk is the proportion of subjects with an event in a total group of susceptible subjects Thus, we can calculate the risk of having a heart attack among smokers (infarcted smokers divided by the total number of smokers) and among nonsmokers (the same, but with nonFrom this contingency table, we can calculate an odds ratio and likelihood ratio Odds Ratio Definition odds ratio – a measure of effect size, describing the strength of association or nonindependence between two binary data values In a case control study, this is the ratio between the fraction with the risk variant versus nonrisk
Odds ratio vs relative riskのギャラリー
各画像をクリックすると、ダウンロードまたは拡大表示できます
 |  |  |
 |  | |
 |  |  |
「Odds ratio vs relative risk」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 |  | |
 |  | |
 |  | |
「Odds ratio vs relative risk」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 |  |  |
 |  | |
 | ||
「Odds ratio vs relative risk」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 |  | |
 |  | |
 |  | |
「Odds ratio vs relative risk」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 |  |  |
 |  |  |
 |  |  |
「Odds ratio vs relative risk」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 |  |  |
 | ||
 |  | |
「Odds ratio vs relative risk」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 |  |  |
 |  |  |
 |  |  |
「Odds ratio vs relative risk」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 |  |  |
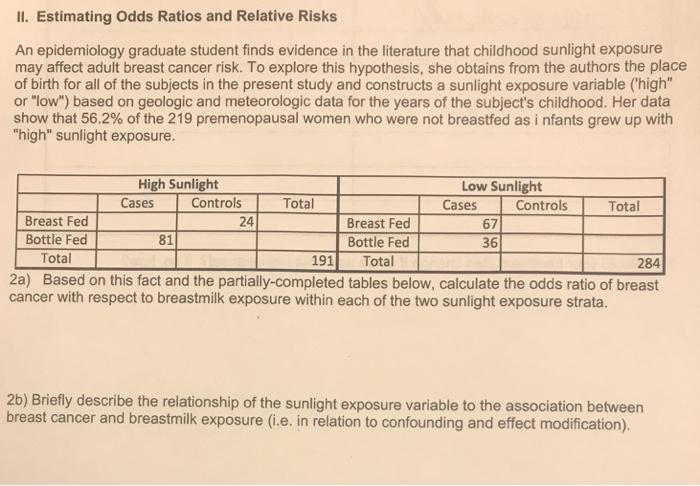 | ||
 |  |  |
「Odds ratio vs relative risk」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
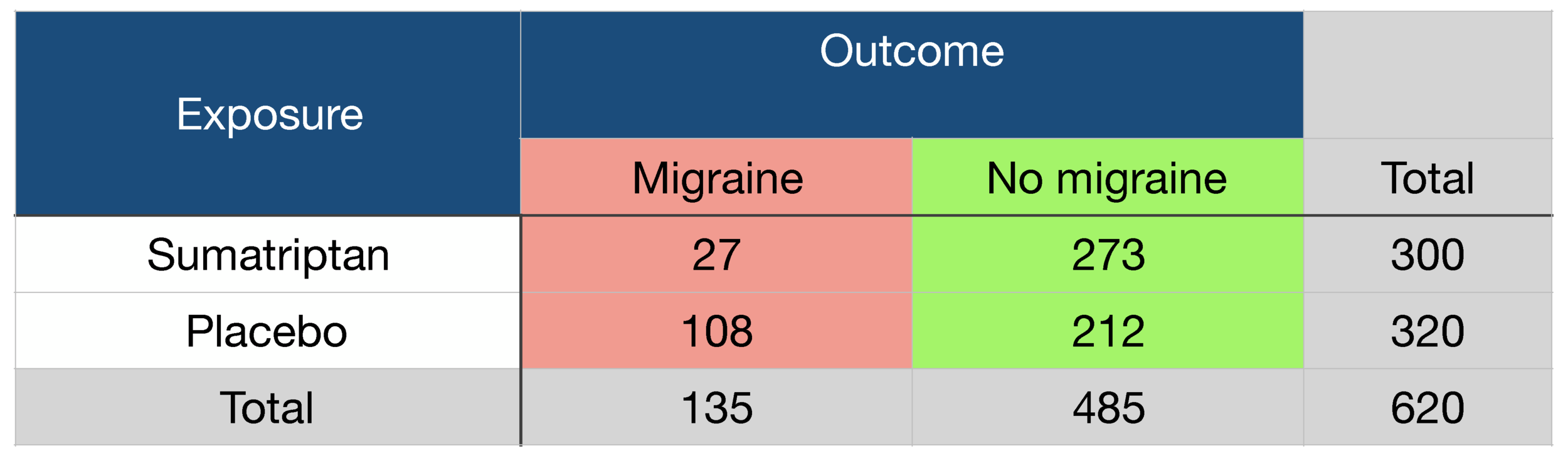 |  |  |
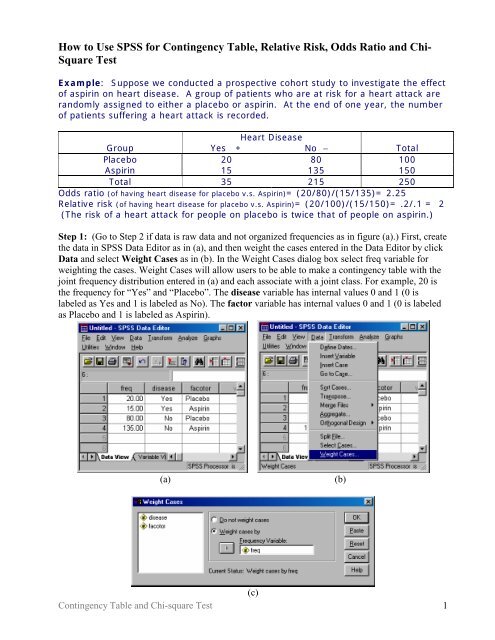 |  |  |
 |  | |
「Odds ratio vs relative risk」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 |  | |
 |  | |
 |  |  |
「Odds ratio vs relative risk」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 |  |  |
 |  | |
 |  |  |
「Odds ratio vs relative risk」の画像ギャラリー、詳細は各画像をクリックしてください。
 |  |  |
 |
Relative Risk (RR) is simply calculated as p (D/M)/p (D/F) For a range of values of these probabilities, the ln (RR) is shown as radii of the circles (if ln (RR) < 0, it is not filled and no circles when ln (RR)=0) Ln (RR) = 0 along the diagonal when p (D/M)=p (D/F) Now, to Odds RatioRelative risk, Risk difference and Odds ratio When the data to be analyzed consist of counts in a crossclassification of two groups (or conditions) and two outcomes, the data can be represented in a fourfold table as follows Several statistics can be calculated such as relative risk and risk difference, relevant in prospective studies, and




